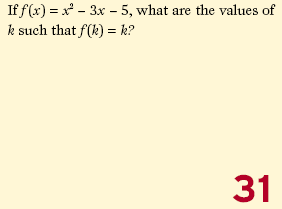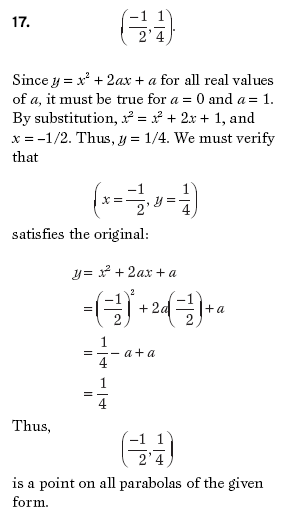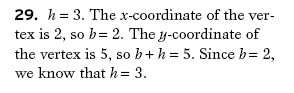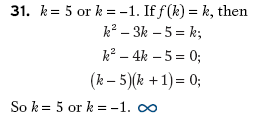Solution 1
Substitute the points  and and  into the given equation for into the given equation for  . .
Then we get a system of two equations:


Subtracting the first equation from the second we have:


Then using  in the first equation: in the first equation:

 is the answer. is the answer.
Solution 2
Alternatively, notice that since the equation is that of a monic parabola, the vertex is likely  . Thus, the form of the equation of the parabola is . Thus, the form of the equation of the parabola is  . Expanding this out, we find that . Expanding this out, we find that  . .
Solution 3
The points given have the same  -value, so the vertex lies on the line -value, so the vertex lies on the line  . .
The  -coordinate of the vertex is also equal to -coordinate of the vertex is also equal to  , so set this equal to , so set this equal to  and solve for and solve for  , given that , given that  : :




Now the equation is of the form  . Now plug in the point . Now plug in the point  and solve for and solve for  : :





|